Sigma
 |
|||
| Greek alphabet | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Αα | Alpha | Νν | Nu |
| Ββ | Beta | Ξξ | Xi |
| Γγ | Gamma | Οο | Omicron |
| Δδ | Delta | Ππ | Pi |
| Εε | Epsilon | Ρρ | Rho |
| Ζζ | Zeta | Σσς | Sigma |
| Ηη | Eta | Ττ | Tau |
| Θθ | Theta | Υυ | Upsilon |
| Ιι | Iota | Φφ | Phi |
| Κκ | Kappa | Χχ | Chi |
| Λλ | Lambda | Ψψ | Psi |
| Μμ | Mu | Ωω | Omega |
| Other characters | |||
| Digamma | Stigma | ||
| Heta | San | ||
| Qoppa | Sampi | ||
| Greek diacritics | |||

Sigma (upper case Σ, lower case σ, lower case in word-final position ς; Greek Σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, and carries the 'S' sound. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 200. When used at the end of a word, and the word is not all upper case, the final form (ς) is used, e.g. Ὀδυσσεύς (Odysseus) - note the two sigmas in the center of the name, and the word-final sigma at the end. It is not to be confused with the cedilla ç.
The letter is ultimately derived from Phoenician Šin 𐤔. However, its name derives from Samekh.
The uppercase form of sigma was borrowed into the Latin alphabet to serve as the uppercase of esh (lowercase: ʃ).
Disigma, or "double sigma", is a non-current term for the character sampi. [1]
Contents |
Lunate sigma
In Eastern forms of Greek writing (as opposed to the Western Greek alphabet used in the European Greek colonies) and in the Middle Ages, the lunate sigma (upper case Ϲ, lower case ϲ) — which resembles, but which is not at all related to, the Latin letter C — was often used. Lunate sigma was frequently used for writing Medieval Greek, and can still be seen in inscriptions in Greek Orthodox churches, and also in certain printed editions of classical authors.
The form of the Cyrillic letter С [s] and Coptic letter sima are derived from lunate sigma.
On coins from the Hellenistic period in India, the script of later coins sometimes use lunate sigma. This sigma continued to be written this way also in Medieval Greek.
A dotted lunate sigma (sigma periestigmenon, encoded at U+03FE Ͼ) was used by Aristarchus of Samothrace as an editorial sign indicating that the line so marked is at an incorrect position. Similarly, an antisigma (encoded at U+03FD Ͻ) may mark a line that is out of place. A dotted antisigma (antisigma periestigmenon, encoded at U+03FF Ͽ) may indicate a line after which rearrangements should be made, or to variant readings of uncertain priority.
Science and mathematics
Upper case Σ is used as a symbol for:
- the summation operator
- a class of baryons in particle physics
- macroscopic cross sections in nuclear and particle physics
- self-energy in condensed matter physics
- the balance of the invoice classes and the overall amount of the debts and demands in economics
- the set of symbols that form an alphabet in linguistics and computer science
Lower case σ is used for:
- sigma bonds in chemistry
- the sigma receptor
- the standard deviation of a population or probability distribution in statistics
- a quality model for business, Six Sigma, based on the standard deviation, often referred to as "6σ"
- sigma-algebras, sigma-fields and sigma-finiteness in measure theory; more generally, the symbol σ serves as a shorthand for "countably", e.g. a σ-compact topological space is one that can be written as a countable union of compact subsets.
- the generated sigma-algebra of a set
 is denoted
is denoted 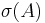
- the sum-of-divisors function in number theory
- the Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- the "sigma factor" of RNA polymerase
- a measure of electrical conductivity
- the Surface charge density in electrostatics
- Normal stress in continuum mechanics
- volatility of a stock generally needed for options pricing
- a syllable in phonology
- the spectrum of a matrix
 , denoted as
, denoted as 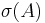 , in applied mathematics
, in applied mathematics - surface tension
- the unary operation of selection on a database relation in relational algebra
- the Pauli matrices in quantum mechanics
- a target's radar cross section (RCS) in radar jamming or Electronic Warfare (EW)
Politics
During the 1930s, an upper case Σ was in use as the symbol of the Ação Integralista Brasileira, a radical right-wing party in Brazil.
Miscellaneous
- Mercury-Atlas 8 was called Sigma 7.
- Upper-case Σ is sometimes substituted jocularly for upper-case E to impart a "Greek" air; posters for the film My Big Fat Greek Wedding and promotional materials for the television series Greek, for instance, have "GRΣΣK" instead.
- Sigma 2,3,5,6,7,8,9 computers produced by Xerox Data Systems in the 1970s following purchase of SDS, Scientific Data Systems, by it. Successful range of scientific computers similar to IBM 370s.
- Sigma is the name of a system for ontology development and reasoning
- Project Sigma was the name of a proposal for a "spontaneous university" by the Scottish writer Alexander Trocchi.
- The French mathematician and poet Jacques Roubaud used the symbol as a title for his first book of poems, Σ, published in 1967.[1]
- The main antagonist in the Mega Man X series is named Sigma.
- In the video game Lux-Pain, Sigma is often mentioned as a power used to destroy "Silent".
- Doctor Who's Ood Sigma was a primary character in Planet of the Ood he also played a minor role in The Waters of Mars and The End of Time. He has the letter Σ on his tunic.
- The last part of the colon in the human body is called " sigmoid" as it is "S" shaped, as it descends down into the pelvis.
See also
- Antisigma
- Sampi
- Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering
References
- ↑ Auster, Paul, editor, The Random House Book of Twentieth-Century French Poetry: with Translations by American and British Poets, New York: Random House, 1982 ISBN 0-394-52197-8